Insights from the Snowflake Security Breach: What We Can Learn!

On May 31st, it was reported that nearly 600 million individuals were affected by two significant breaches. Ticketing giant Ticketmaster and the bank Santander disclosed they had fallen victim to large-scale breaches, impacting 560 million and 30 million users (about the population of Texas) respectively. The breaches were facilitated through a targeted attack on Ticketmaster and Santander’s third-party SaaS cloud storage provider, Snowflake. While investigations are ongoing, initial reports suggest that hundreds of millions of records have been compromised. Notably, the threat actor responsible claims to have accessed data from approximately 400 organizations.
In this blog post, we delve into the details of the Snowflake breach, underscoring the critical importance of implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and effective password policies. Furthermore, we explore how CheckRed’s SaaS Security Posture Management platform (SSPM) can elevate security standards while ensuring a smooth and intuitive user experience.
Breach Synopsis: The Sequence of Events
The Snowflake data breach highlighted significant weaknesses in customer account security, prompting serious concerns about safeguarding sensitive data. How did such a large-scale breach occur? Let’s explore how threat actors driven by financial motives obtained credentials and the key factors that led to this security incident.
How did the unauthorized access to accounts occur?
The attackers utilized credentials that had been compromised earlier to illicitly access Snowflake customer accounts. These credentials were probably acquired through infostealer malware or from past data breaches. According to investigations by Mandiant and Snowflake, approximately 80% of the compromised accounts had credentials that were previously exposed.
Subsequently, the threat actors employed custom tools to conduct reconnaissance within the Snowflake platform, gathering information such as organization names, users, roles, and IP addresses. Once inside, they executed SQL commands to extract data from the compromised customer accounts.
Let’s explore what aided the attackers in gaining access
Snowflake accounts were left dangerously vulnerable due to several security oversights, effectively creating opportunities for cybercriminals. Let’s examine the primary security loopholes:
Insufficient authentication measures
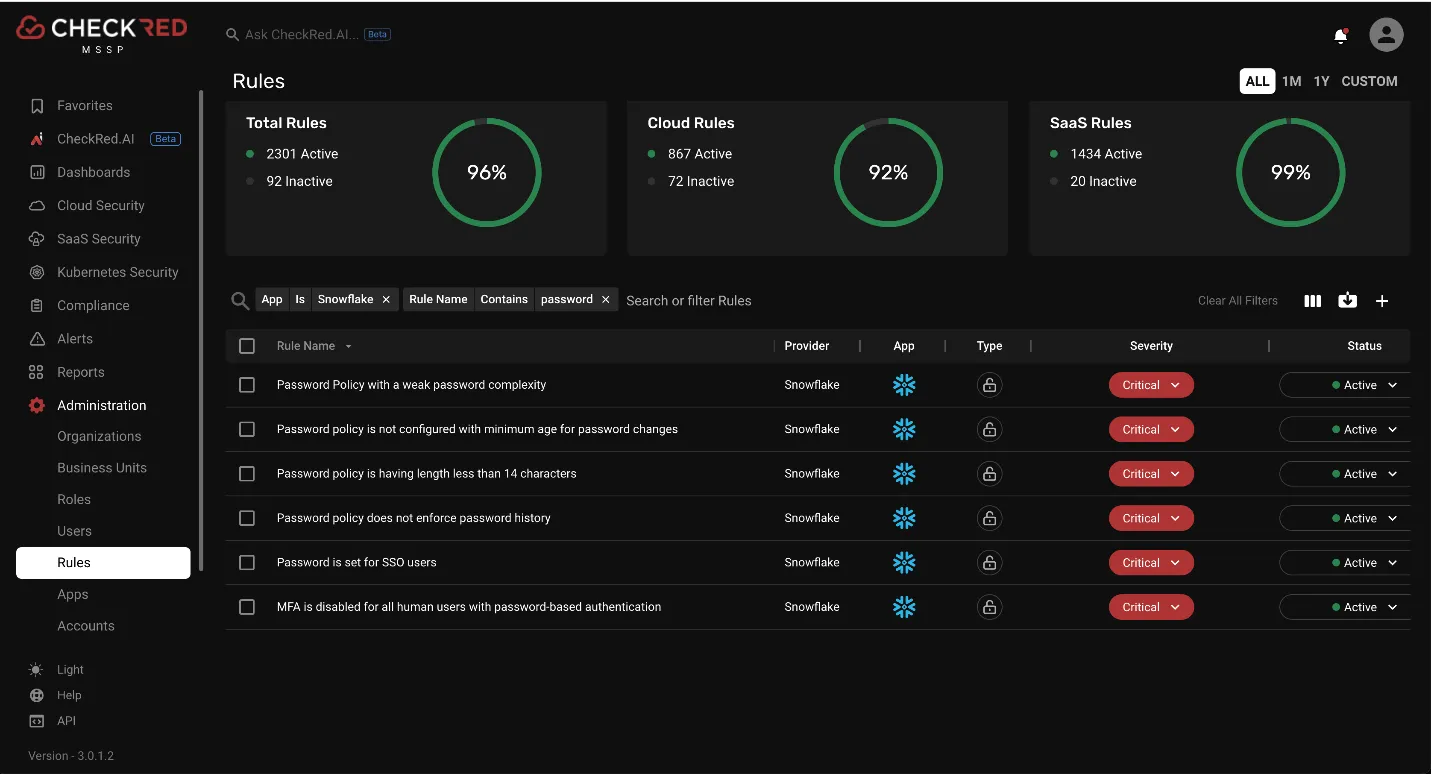
The compromised accounts lacked multi-factor authentication (MFA) and SSO, relying solely on single-factor authentication. Snowflake has since stressed the importance of implementing MFA across all customer accounts to prevent similar breaches in the future, although it is currently not mandatory.
Outdated credentials
A concerning number of stolen credentials were outdated, some even several years old, highlighting a significant lapse in regular password updating practices. Regular credential updating is essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
Snowflake has recommended the security policy configurations as below:
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication on all accounts;
- Set up Network Policy Rules to only allow authorized users or only allow traffic from trusted locations (VPN, Cloud workload NAT, etc.); and
- Impacted organizations should reset and rotate Snowflake credentials.
How CheckRed can help
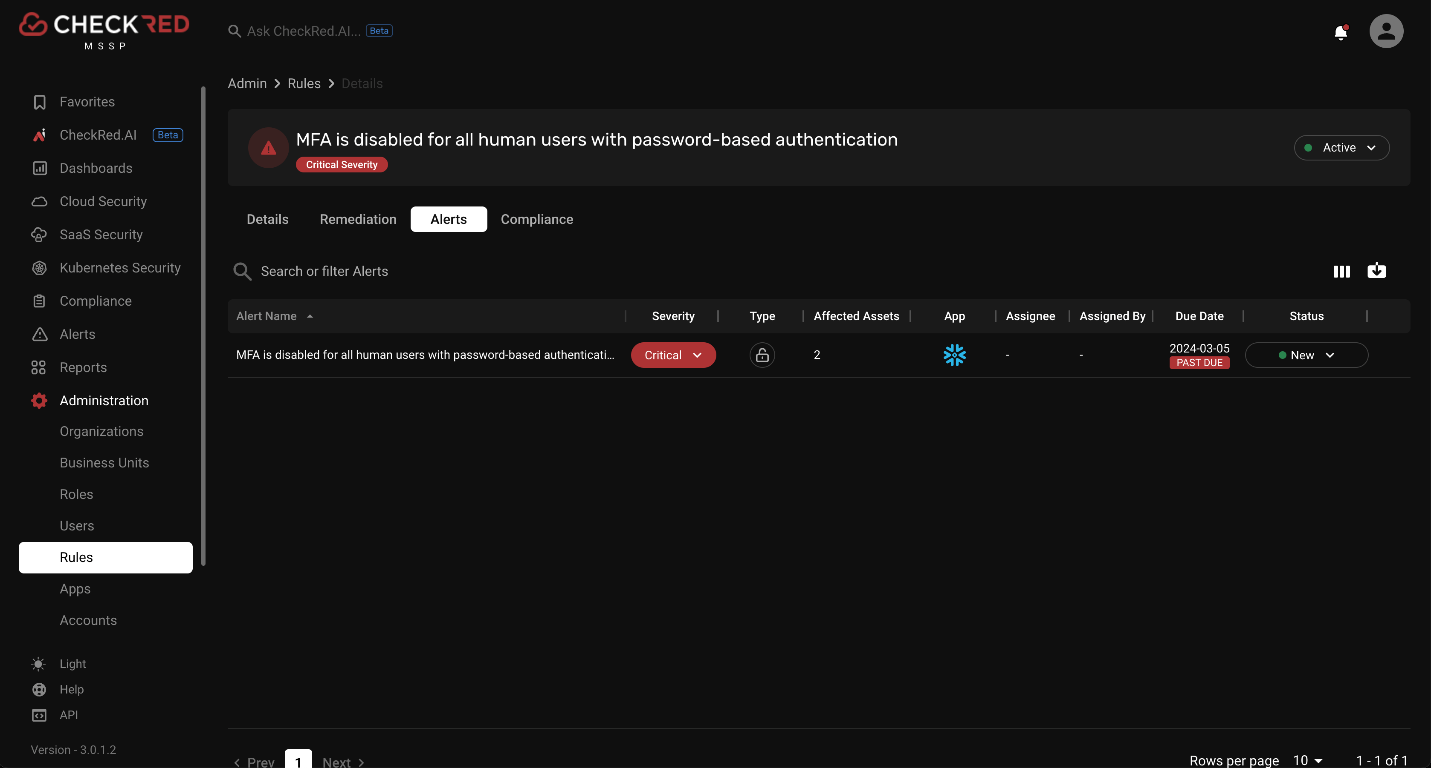
CheckRed’s SaaS security posture management platform enables automatic detection of security configurations and provides alerts if these specific policies are violated.
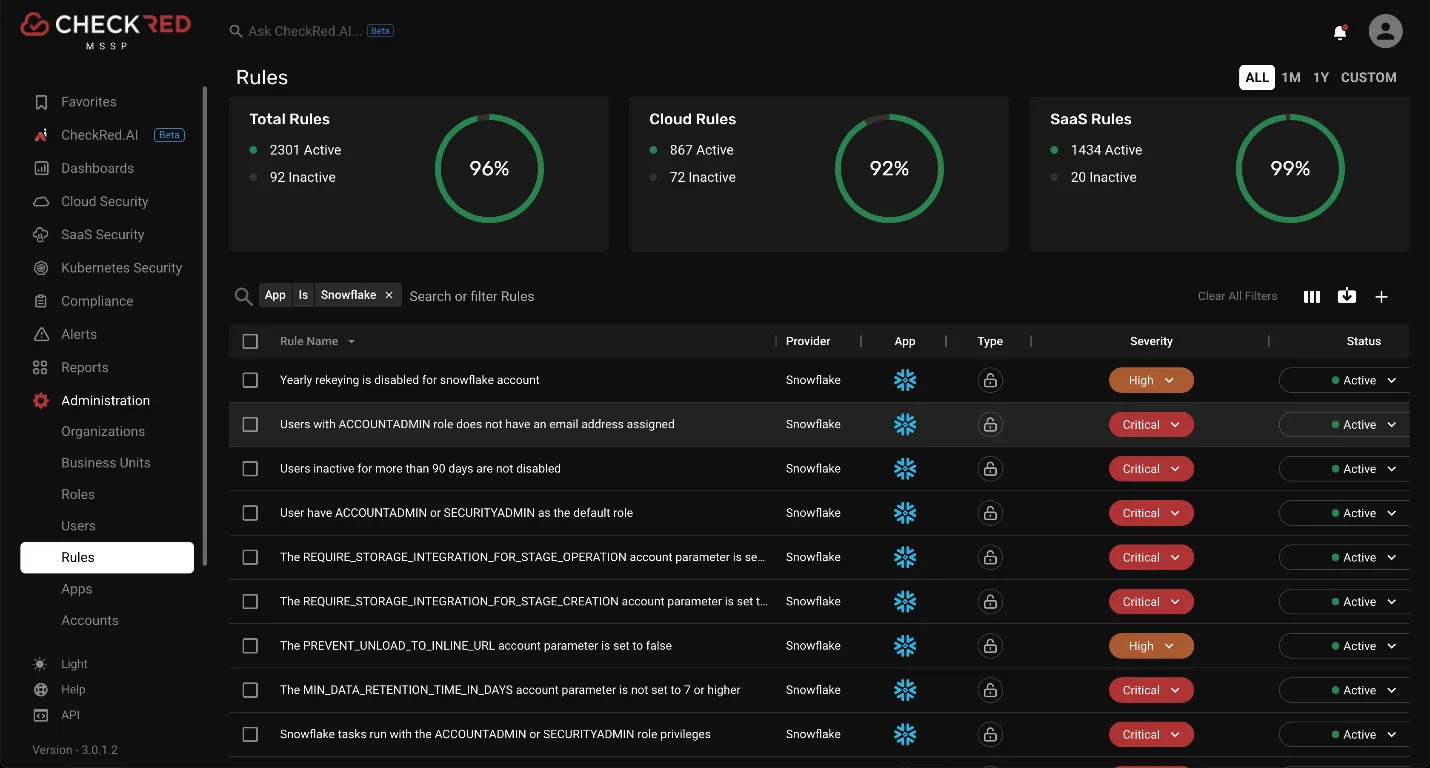
Onboarding Snowflake and performing security configuration assessments for Snowflake are one-click tasks for the security team. CheckRed offers comprehensive security policies that ensure the overall security of a Snowflake application.
Source Reference: Integration with Snowflake
Source Reference: Policies covered for Snowflake application
Source Reference: Password policies
Source Reference: Alert generated after violation of a policy
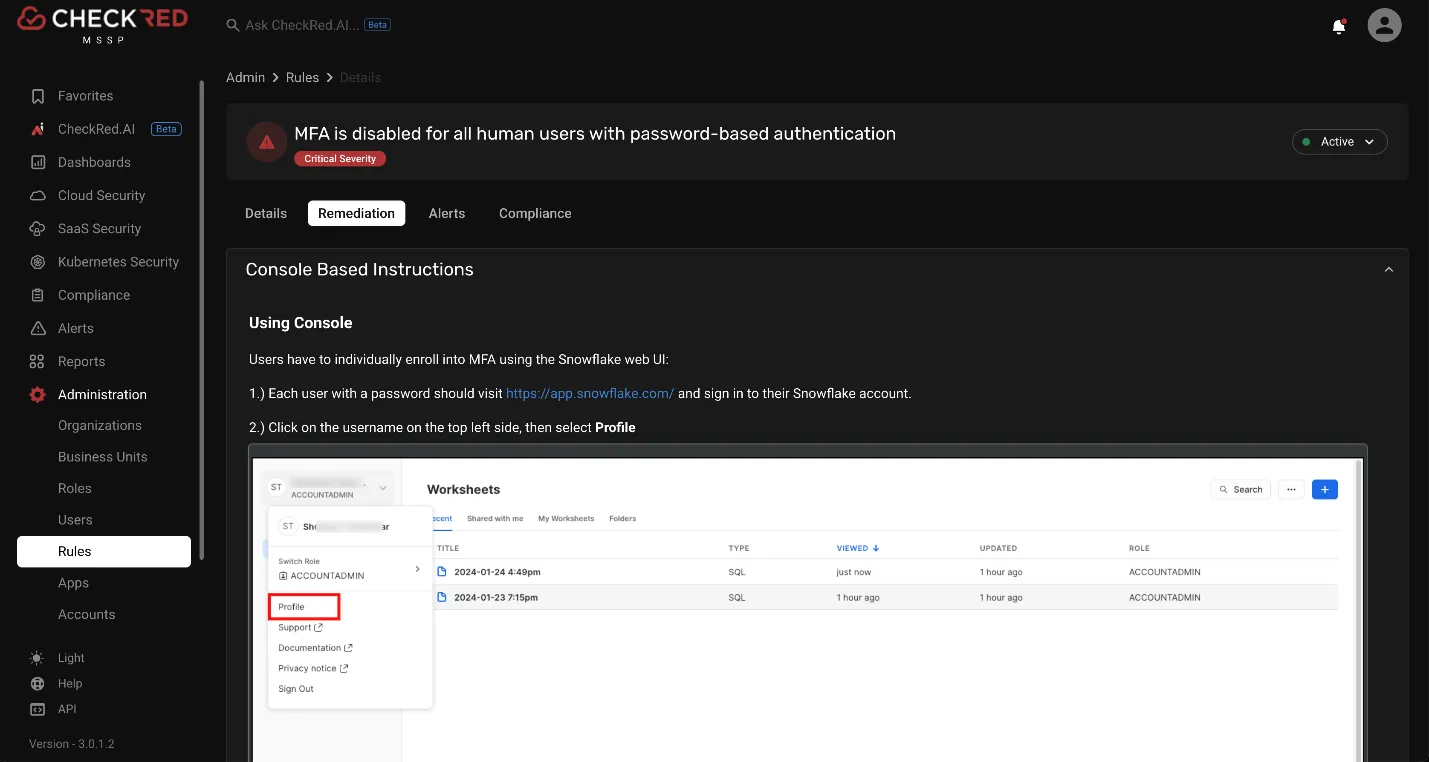
Source Reference: Remediation instructions.
CheckRed not only detects security violations and sends alerts but also guides the security team on how to fix or remediate these issues by providing step-by-step remediation instructions. Additionally, CheckRed ensures continuous audit readiness by offering extensive compliance framework support, including HIPAA, NIST 800-53, PCI-DSS 3.2, 4.0, and more. Furthermore, CheckRed’s dynamic reporting capabilities enable end users to generate evidence of compliance effortlessly.
By leveraging CheckRed’s comprehensive tools and capabilities, organizations can confidently manage their Snowflake –and more than 25+ other SaaS applications, with enhanced security, efficiency, and compliance readiness.